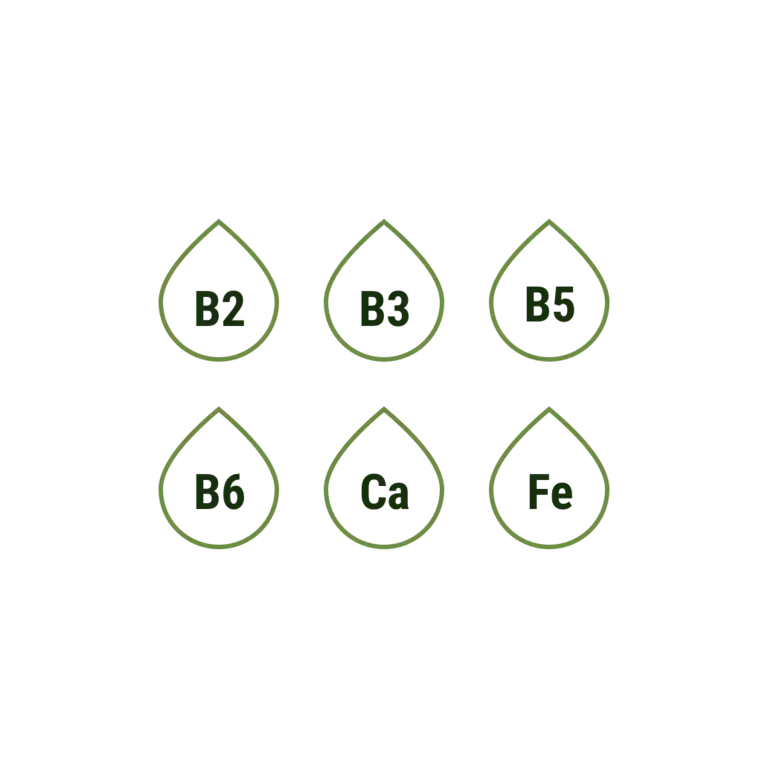
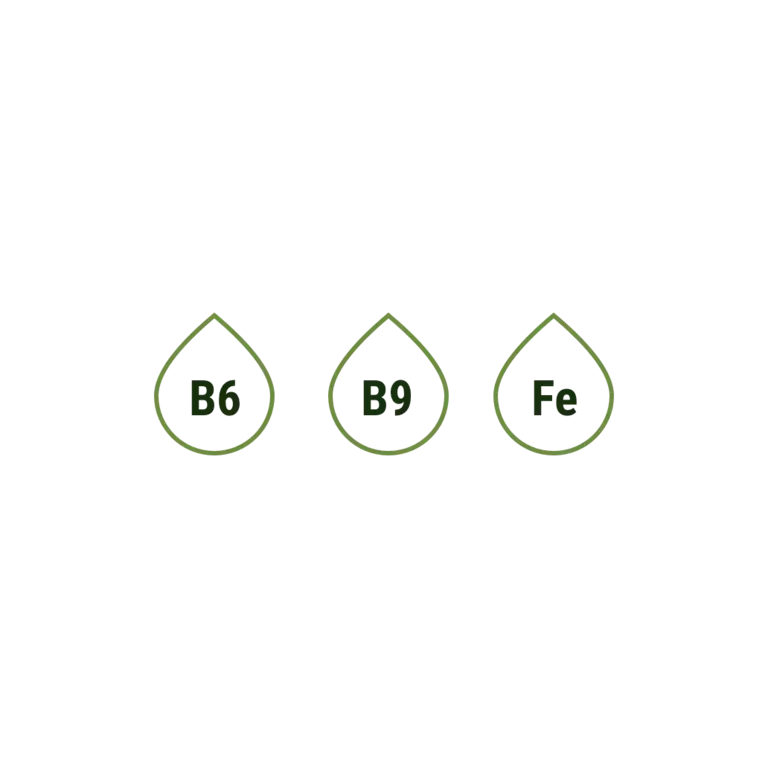
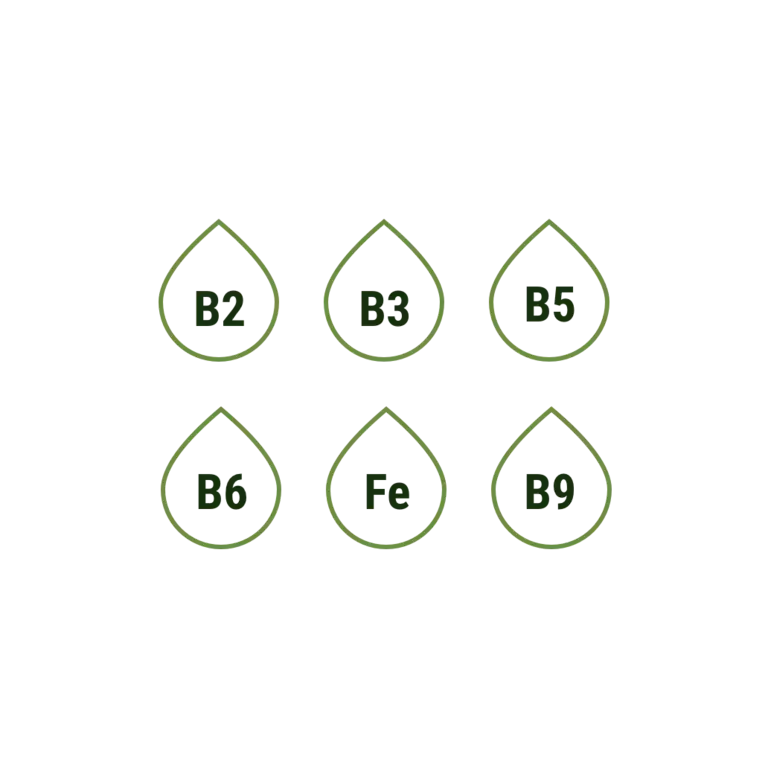
The word ‘fortification’ means ‘a defensive wall or other reinforcement built to strengthen a place against attack’ – so what has that got to do with cereals? Well, when cereals are ‘fortified’, it means they contain added vitamins and minerals to help our body work well.